Introduction : The incidence of HIV-positive lymphoma remains significantly higher than HIV-negative patients in the era of combined antiretroviral therapy(cART). DLBCL is the most common histological type of HIV-positive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma(NHL). Exportin 1 protein(XPO1) inhibitor has demonstrated preliminary anti-HIV activity and synergy with anti-lymphoma drug(e.g. etoposide, doxorubicin, prednisone).
Methods: The study was designed to evaluate safety and efficacy of selinexor (60mg Days 1, 8, 15) combined with R-EPOCH(rituximab 375 mg/m2d1, etoposide 50 mg/m2 d1-d4, doxorubicin 10mg/m2 d1-d4, vinblastine 0.4mg/m2 d1-d4, prednisone 60mg/m2 d1-d5 and cyclophosphamide 750mg/m2 d5) every 3 weeks (4-6 cycles), followed by selinexor maintenance (60 mg weekly) or transplantation as per physician's choice in patients with untreated HIV-positive DLBCL. All patients received cART concomitantly during chemotherapy. This study was registered at Chictr.org.cn(ChiCTR2300069941).
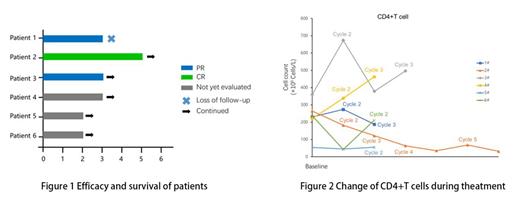
Results: From Feb 24, 2023 to July 17, 2023, 6 patients were enrolled and received at least one cycles of study treatment. Median age was 55 years (range 43-67) with four patients(66.7%) was male. All six patients were in advanced stage according to Ann Arbor staging system, with aaIPI intermediate to high risk or IPI low to intermediate risk. Four patients(66.7%) were germinal center B-cell-like lymphoma (GCB) subtype and three patients(50%) had an Elevated lactate dehydrogenase level. Median HIV RNA load was 74450(10000-100000) copies/mL and Median CD4 cell count was 233 cells/μL (233 cells/mm3) with one patient having a CD4 cell count less than 200 cells/μL (200 cells/mm3). Two patients were HBV-positive and one was EB virus(EBV) coinfection at baseline.
Three patients achieved PR after two treatment cycles, one patient of which had completed five treatment cycles and achieved complete response at the end of the fourth cycle (Figure 1). One patients after interim evaluation with PR stopped treatment because of loss to follow-up. The EBV DNA load of the patient with EBV coinfection at baseline turned to normal level after one treatment cycle. Similar result was observed in two HBV-positive patients, the one achieved HBV-negative after two cycles and the other's HBV DNA load level declined from 7.96×10^4 IU/mL to 1.12×10^3 after completing first cycle. HIV RNA load of the patient with CR had declined to <20 copies/mL from 58300 copies/mL after the fourth cycle, another patient likewise became HIV-negative before the initiation of the third cycle. The change of CD4+T cell count during treatment was presented in Figure 2.
All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE), 3 (50%) patients with at least one Grade≥3 TEAE. The most common grade 3 or 4 adverse events were hematological toxicities including lymphopenia(83.3%), neutropenia (50%), leukopenia(33.3%), thrombocytopenia (33.3%). Two patients experienced Febrile neutropenia. The non-hematological toxicities were grade 1 or 2, including nausea(66.7%), vomit(50%), constipation(33.3%), cough(33%). One patient stopped treatment for one month due to pulmonary infection. All toxicities were manageable by supportive care.
Conclusion: Selinexor plus R-EPOCH regimen demonstrated a favorable Interim efficacy and manageable safety profile in patients with HIV-associated DLBCL. The change of HIV RNA load and CD4+ cell count still requires further evaluation.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.